Torque and moment of inertia gizmo answer key – Delving into the realm of torque and moment of inertia, this guide unlocks the mysteries surrounding these fundamental concepts through the lens of the Gizmo simulation. Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey that unravels the intricate relationship between rotational motion, torque, and moment of inertia, leaving you with a profound understanding of their practical applications in the world around us.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the precise definition of torque, its role in causing objects to rotate, and encounter real-world examples that showcase its ubiquitous presence in our daily lives. Subsequently, we will unravel the concept of moment of inertia, a crucial measure of an object’s resistance to rotational motion, and uncover the factors that influence its magnitude.
Definition of Torque
Torque is a force that causes an object to rotate about an axis. It is measured in newton-meters (N·m) and is calculated as the product of the force applied to the object and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the point where the force is applied.
Torque is commonly encountered in everyday situations, such as when opening a door, tightening a screw, or pedaling a bicycle.
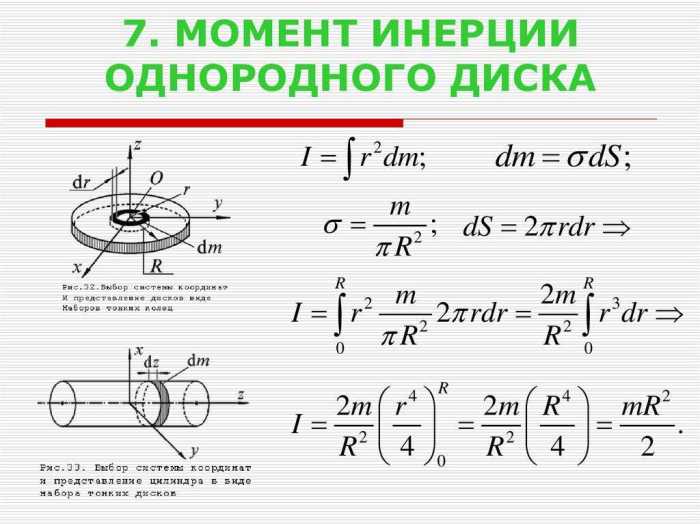
Definition of Moment of Inertia
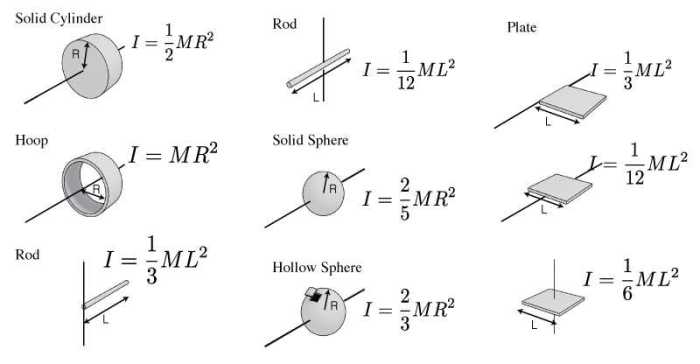
Moment of inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to rotational motion. It is calculated as the sum of the products of the mass of each particle in the object and the square of its distance from the axis of rotation.
The moment of inertia depends on the object’s mass, shape, and distribution of mass.
Relationship between Torque and Moment of Inertia
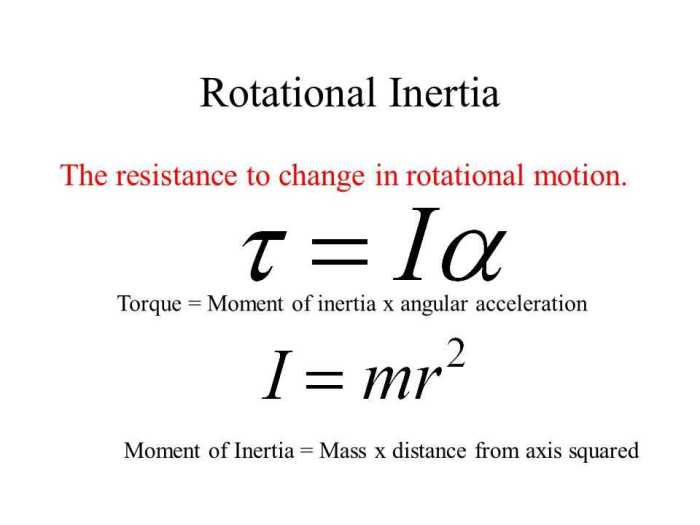
The relationship between torque and moment of inertia is given by the following equation:
τ = Iα
where:
- τ is the torque applied to the object
- I is the moment of inertia of the object
- α is the angular acceleration of the object
This equation shows that the torque applied to an object is directly proportional to its angular acceleration. The greater the torque, the greater the angular acceleration.
Gizmo Simulation
The Gizmo simulation can be used to investigate the relationship between torque and moment of inertia.
The simulation allows you to manipulate the following variables:
- The mass of the object
- The radius of the object
- The torque applied to the object
By manipulating these variables, you can see how they affect the object’s angular acceleration.
Applications of Torque and Moment of Inertia: Torque And Moment Of Inertia Gizmo Answer Key

Torque and moment of inertia have many practical applications in engineering and everyday life.
Some examples include:
- The design of engines and other rotating machinery
- The analysis of the stability of structures
- The design of sports equipment
- The analysis of human movement
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of torque in everyday life?
Torque plays a crucial role in various everyday activities, such as opening a door, tightening a screw, or riding a bicycle. It enables us to apply force to rotate objects around a fixed axis, making it an essential concept in mechanics.
How does moment of inertia affect the motion of an object?
Moment of inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to rotational motion. A higher moment of inertia indicates greater resistance, making it more difficult to accelerate or decelerate the object’s rotation.
What are some practical applications of torque and moment of inertia?
Torque and moment of inertia find applications in diverse fields, including engineering, sports, and transportation. They are essential for designing efficient machines, analyzing the dynamics of sports equipment, and understanding the stability of vehicles.