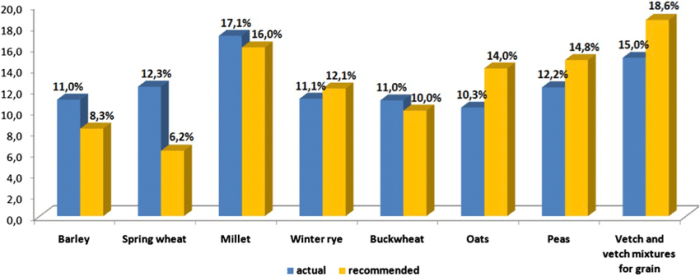
Which of the following crops is grown at lower elevations? This question sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the fascinating world of crop cultivation, we will explore the intricate relationship between elevation and crop growth, uncovering the secrets that determine which crops flourish in the lowlands.
Elevation plays a pivotal role in shaping the environmental conditions that crops encounter. Temperature, sunlight, and precipitation all vary with elevation, creating unique microclimates that favor specific plant species. In this article, we will identify the specific crops that are commonly cultivated at lower elevations, examining the reasons why these crops are ideally suited to these environments.
Crop Cultivation and Elevation
The elevation of a crop’s growing area significantly influences its growth and productivity. Elevation affects various environmental factors that are crucial for plant development, including temperature, sunlight, and precipitation.
At higher elevations, temperatures tend to be cooler, sunlight intensity is lower, and precipitation is often more frequent. These conditions favor the growth of certain crops, such as potatoes, leafy greens, and berries.
In contrast, lower elevations typically experience warmer temperatures, higher sunlight intensity, and less frequent precipitation. These conditions are more suitable for crops that require ample heat and sunlight, such as corn, soybeans, and tomatoes.
Crops Grown at Lower Elevations, Which of the following crops is grown at lower elevations
The following crops are commonly cultivated at lower elevations due to their adaptability to warmer temperatures and higher sunlight intensity:
- Corn: Thrives in warm, humid conditions with ample sunlight.
- Soybeans: Prefers well-drained soils and moderate temperatures.
- Tomatoes: Requires abundant sunlight and warm, dry conditions.
- Cotton: Tolerates high temperatures and requires long growing seasons.
- Sugarcane: Grows best in tropical and subtropical regions with high rainfall.
- Rice: Adapted to warm, humid climates and can tolerate flooding.
Factors Affecting Crop Selection at Lower Elevations
When selecting crops for cultivation at lower elevations, farmers consider several environmental factors:
- Temperature: Crops that require warm temperatures, such as corn and tomatoes, are well-suited for lower elevations.
- Humidity: High humidity can favor disease development in crops, so farmers may opt for drought-tolerant varieties.
- Soil type: Well-drained soils are ideal for most crops, but some, such as rice, can tolerate flooded conditions.
Case Studies and Best Practices
Successful crop cultivation at lower elevations requires careful management and adherence to best practices:
- Crop rotation: Alternating different crops in a field helps maintain soil health and reduce disease incidence.
- Irrigation: Regular irrigation is essential in areas with low rainfall to ensure adequate water supply.
- Fertilization: Soil testing helps determine the specific nutrient requirements of crops, ensuring optimal growth.
- Pest and disease management: Integrated pest management strategies minimize crop losses due to pests and diseases.
Essential Questionnaire: Which Of The Following Crops Is Grown At Lower Elevations
What factors influence crop selection at lower elevations?
Temperature, humidity, soil type, and precipitation are key factors that farmers consider when choosing crops for lower elevations.
Why are certain crops better suited for lower elevations?
Crops that thrive at lower elevations are typically adapted to warmer temperatures, higher humidity, and specific soil conditions found in these areas.
What are some examples of crops commonly grown at lower elevations?
Rice, sugarcane, bananas, and citrus fruits are among the many crops that are well-suited to lower elevations.