American imperialism crash course us history #28 transcript – Embarking on an exploration of American imperialism, this transcript from Crash Course US History #28 delves into the motivations, key events, and lasting impact of the United States’ expansionist policies.
Unveiling the historical context, major acquisitions, and methods of control employed by the United States, this transcript provides a comprehensive overview of American imperialism.
Historical Context of American Imperialism
The late 19th century witnessed the rise of American imperialism, driven by a complex interplay of economic, political, and cultural factors. The rapid industrialization of the United States created an insatiable demand for raw materials and new markets, fueling expansionist desires.
National pride and a sense of manifest destiny further propelled the nation towards global influence.
Key Events and Territories Acquired: American Imperialism Crash Course Us History #28 Transcript

The Spanish-American War of 1898 marked a turning point in American imperialism. The war resulted in the acquisition of Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines, establishing the United States as a major colonial power. The annexation of Hawaii in 1898 further expanded American presence in the Pacific.
Methods of Imperial Control, American imperialism crash course us history #28 transcript
The United States employed various methods to establish and maintain control over its overseas territories. Military force was used to suppress resistance and establish order. Economic dominance, through the establishment of preferential trade agreements and the exploitation of natural resources, ensured economic control.
Cultural assimilation policies aimed to reshape the indigenous cultures of the territories in line with American values and norms.
Impact on the United States
American imperialism had a profound impact on the domestic and foreign policies of the United States. The acquisition of overseas territories expanded American economic power and enhanced its global influence. However, it also led to increased military spending and the rise of anti-imperialist sentiment within the country.
Impact on the Territories Acquired
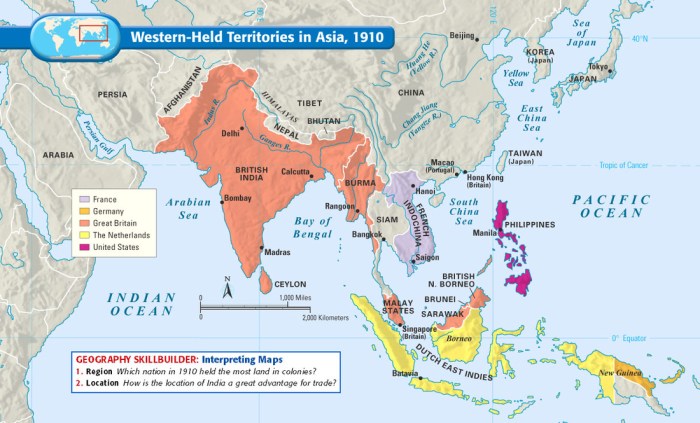
The indigenous populations of the territories acquired faced significant cultural, economic, and political changes under American rule. Americanization policies attempted to reshape local cultures, while economic exploitation often led to the displacement of indigenous peoples from their traditional lands. The introduction of American political systems and institutions brought both opportunities and challenges for the local populations.
Legacy and Criticism

The legacy of American imperialism continues to be debated today. Some argue that it was a necessary step in the nation’s rise to global power, while others condemn it as a form of colonialism and oppression. The ongoing criticism of American imperialism highlights the complex and controversial nature of this historical period.
Essential FAQs
What were the primary motivations for American imperialism?
Economic expansion, national pride, and the desire for global influence were key driving forces behind American imperialism.
What were some of the key events in the period of American imperialism?
The Spanish-American War, the annexation of Hawaii, and the acquisition of the Philippines, Guam, and Puerto Rico were significant events during this period.
How did the United States establish and maintain control over its overseas territories?
The United States employed a combination of military force, economic dominance, and cultural assimilation to establish and maintain control over its overseas territories.

