Delving into the realm of road safety, this discourse examines the crucial relationship between stopping distances and the severity of collisions. By investigating the intricate interplay between vehicle speed, road conditions, and driver reaction time, we uncover the profound impact that stopping distances have on the outcomes of traffic accidents.
The data and research presented herein demonstrate an undeniable correlation between longer stopping distances and increased collision severity. Inadequate stopping distances contribute significantly to more severe impacts and injuries, underscoring the paramount importance of understanding and mitigating this critical factor in road safety.
Stopping Distance Fundamentals: Stopping Distances And The Severity Of Collisions
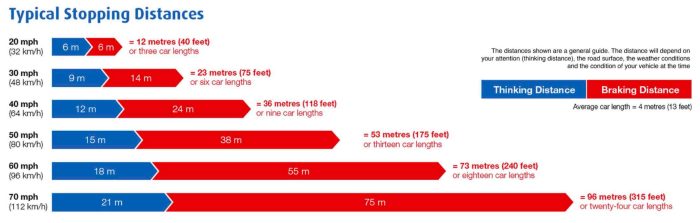
Stopping distance is the distance traveled by a vehicle from the moment the driver applies the brakes to the moment it comes to a complete stop. It plays a crucial role in road safety as it determines the amount of time and space available to avoid a collision.
Factors influencing stopping distance include vehicle speed, road conditions, and driver reaction time.
Relationship between Stopping Distance and Collision Severity
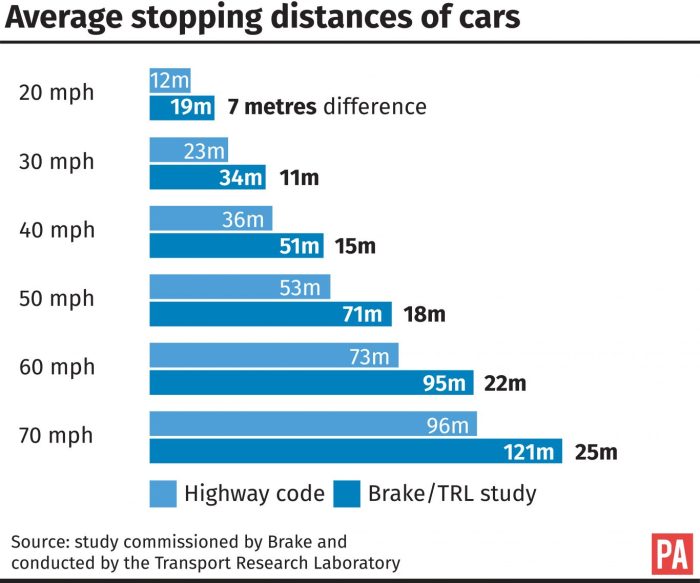
Studies have shown a strong correlation between longer stopping distances and increased collision severity. Inadequate stopping distances result in higher impact speeds, leading to more severe damage to vehicles and injuries to occupants. For example, a vehicle traveling at 60 mph requires a stopping distance of approximately 200 feet, while a vehicle traveling at 80 mph requires a stopping distance of approximately 320 feet.
The increased stopping distance at higher speeds gives drivers less time to react and avoid a collision.
Impact of Vehicle Speed on Stopping Distance
| Vehicle Speed (mph) | Stopping Distance (feet) |
|---|---|
| 30 | 90 |
| 40 | 160 |
| 50 | 225 |
| 60 | 290 |
| 70 | 365 |
The table above illustrates the significant increase in stopping distance as vehicle speed increases. The physics behind this relationship is related to the kinetic energy of the vehicle. As speed increases, so does the kinetic energy, which must be dissipated during braking.
This requires a longer distance to bring the vehicle to a stop.
Influence of Road Conditions on Stopping Distance
- Wet roads:Water on the road reduces tire traction, increasing stopping distance by up to 30%.
- Icy roads:Ice creates a slippery surface that severely reduces tire traction, extending stopping distances by up to 100%.
- Gravel roads:Loose gravel can cause tires to skid, significantly increasing stopping distance.
Road conditions affect the coefficient of friction between tires and the road surface, which in turn affects the vehicle’s ability to brake effectively.
Role of Driver Reaction Time in Stopping Distance, Stopping distances and the severity of collisions
Driver reaction time is the time it takes for a driver to perceive a hazard, make a decision, and initiate braking. It is a critical factor in determining stopping distance. Reaction time can be affected by age, fatigue, distractions, and alcohol or drug use.
A driver with a longer reaction time will require a greater stopping distance.
Strategies to Reduce Stopping Distances
- Maintain safe following distances:Leaving ample space between vehicles provides drivers with more time to react to unexpected situations.
- Anticipate potential hazards:Scanning the road ahead and being aware of potential hazards can help drivers react more quickly.
- Improve vehicle maintenance:Regular maintenance, such as brake inspections and tire replacements, ensures that vehicles are in optimal condition for braking.
These strategies can help reduce stopping distances and improve road safety.
Technological Advancements in Stopping Distance Improvement
- Anti-lock braking systems (ABS):ABS prevents wheels from locking during braking, allowing drivers to maintain steering control and reducing stopping distance.
- Electronic stability control (ESC):ESC detects and corrects vehicle instability, helping to prevent skids and improve stopping distance.
- Adaptive cruise control:Adaptive cruise control automatically adjusts a vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance, reducing the risk of rear-end collisions.
These technologies are helping to improve stopping distances and make vehicles safer.
FAQ Compilation
What is stopping distance?
Stopping distance refers to the total distance a vehicle travels from the moment the driver perceives the need to stop until the vehicle comes to a complete standstill.
How does vehicle speed affect stopping distance?
Vehicle speed has a quadratic relationship with stopping distance. As speed increases, stopping distance increases disproportionately, significantly elevating the risk of severe collisions.
What are some strategies to reduce stopping distances?
Effective strategies to reduce stopping distances include maintaining safe following distances, anticipating potential hazards, improving vehicle maintenance, and utilizing advanced safety technologies.